Looking for answers to “What is DeFi?” Look no further. This post will answer most, if not all, your questions about DeFi!
DeFi is a collective term for financial products and services accessible to anyone on the internet via Blockchain applications.
Smart contracts run DeFi applications, with the first smart contracts executed on the Ethereum blockchain. Now there are over 100 blockchains that support smart contracts and offer money making DeFi applications. Some include Arbitrum, Avalanche, Polygon, Fantom, Cardano, Solana, Stellar and many more.
Smart contracts are often called programmable money. The smart contract code is publicly available, so anyone with the proper knowledge can review it.
Using DeFi applications to stake, provide liquidity, borrow crypto, or loan crypto to earn rewards is like being your own printing press. In fact, the yield farming community calls earning rewards printing money. I must admit it’s pretty fun!
Watch this short 2 minute video 🎞️ on DeFi. It does an excellent job explaining it. 👇
Let’s look at Traditional vs. Decentralized Finance and consider how their products and services are different or similar.
Traditional Financial (TradFi) Products and Services
TradFi, or Traditional Finance, is the mainstream financial system characterized by a high degree of centralization, control and exclusivity. It refers to traditional retail, commercial and investment banks. The term TradFi evolved in order to contrast traditional centralized financial services with crypto decentralized financial services (DeFi).
TradFi Banking Products/Services
- Checking/saving accounts
- Mortgages
- Loans
- Credit cards
- Wire transfers
- Money market accounts
- Certificates of Deposit
TradFi Investment Products/Services
- Stock market
- Bond market
- Forex market
- Online brokers
- Robo-advisors
Other TradFi Products/Services
- Insurance products
- Tax and Accounting services
Decentralized Financial (DeFi) Products and Services
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging financial technology based on secure distributed ledgers and smart contracts. DeFi challenges the centralized TradFi financial system by empowering individuals with peer-to-peer digital exchanges plus lending and borrowing platforms.
DeFi eliminates the fees that banks and other financial companies charge for using their services. Individuals hold money in a secure digital wallet, can transfer funds in minutes, and anyone with an internet connection can use DeFi applications.
Just to let you know, using DeFi applications isn’t free. Transaction fees (called gas) must be paid to blockchain validators. Depending on network traffic, fees can range between 10 cents to $20 or even higher. Luckily, if fees are too high, wait a while, and they will probably be lower.
DeFi Banking Products/Services
- Stablecoins (can’t use USD but can use USDC, a collateralized stablecoin created by Circle and Coinbase)
- Personal (self-custody) wallets manage your money.
- Custodial wallets, similar to TradFi bank accounts, control your crypto. Usually, centralized exchanges – meaning a corporation manages your money. Example: Coinbase or Kraken
- Loans – Borrowing and Lending
DeFi Investment Products/Services
- Centralized exchange (CEX) crypto market
- Online exchanges where crypto holders can swap cryptocoins using a custodial wallet
- Or sell crypto into fiat currency
- This is an active income strategy
- Decentralized exchange (DEX) crypto market
- Blockchain applications that use smart contracts to allow trading between token holders
- This is an active income strategy
- Staking – kind of like a certificate of deposit
- Staking crypto on a proof of stake blockchain earns interest (aka rewards)
- This is a passive income strategy.
- Liquidity provider – this is how a DEX works.
- Individuals like you and I deposit our cryptocoins to the DEX and receive interest (aka rewards) for providing liquidity to trading markets.
- This is a passive income strategy.
- Yield Farming – a collective term referring to crypto holders who maximize rewards across various DeFi platforms by engaging in lending, borrowing, or staking cryptocoins.
- Sometimes called yield optimization.
- This is a passive income strategy.
DeFi Insurance Products/Services
- DeFi insurance coverage against black swan events or other losses caused by events in the DeFi industry
- DeFi insurance coverage is available for
- Exchange hacks
- DeFi protocol attacks
- Smart contract failures
- Stablecoin price de-pegging
Why Use DeFi?
- Accessibility – Many people can’t get a bank account but can use crypto if they have internet and a smartphone.
- Increased transparency and security compared to TradFi products and services; however transparency and security sacrifices some privacy.
- Low fees on transactions except during heavy volume
- High-interest rates on investments! Much higher than anywhere else.
- Autonomy – DeFi platforms don’t rely on centralized institutions, which may go bankrupt or close your accounts for no reason. This is a major problem in the world of TradFi today.
DeFi Challenges
- Poor performance – Blockchains can be slow. However, it’s all relative. Compared to wiring funds through a bank, blockchain transactions are fast. But sometimes blockchain networks become congested from heavy use, and this causes transactions to process more slowly.
- High risk of user error – There’s much detail in crypto. Losing one’s focus and clicking the wrong thing could cause a loss of funds.
- Bad user experience – Some DeFi applications need design help, better instructions, and more user support. It’s good to have friends that are crypto-savvy in order to ask questions.
- Cluttered ecosystem – There are so many options in DeFi that it can be challenging to decide which application to use. In each category, there are tons from which to choose. Like DEXs, bridges, lending platforms, and yield farming platforms.
DeFi Risks
- Counterparty Risk: If you take part in crypto loans or any other lending, you’re at risk of the counterparty not repaying their debt.
- Regulatory Risk: If a smart contract gets shut down due to regulatory problems, your funds may be at risk.
- Token Risk: Crypto assets have different levels of risk based on liquidity, trustworthiness, and smart contract security, as well as the project and team. Because the DeFi space has many low market-cap cryptos, token risk can be exceptionally high.
- Software Risk: Code vulnerabilities could undermine the security of smart contracts running on a blockchain.
- Impermanent Loss: If you’re staking in liquidity pools, impermanent loss may cause a position to lose money.
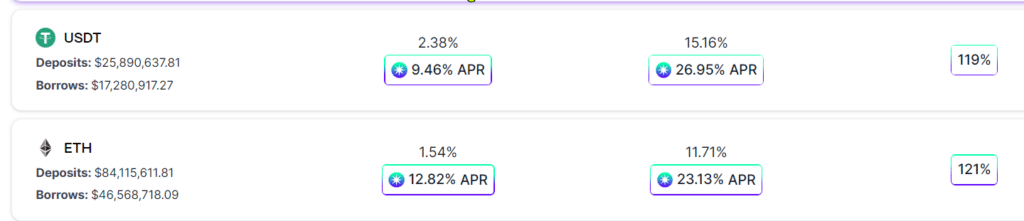
DeFi Example
Below is a screenshot from Radiant Capital, a lending and borrowing platform. The left column shows the interest rates for rewards paid on depositing either USDT or ETH to the platform. If USDT is deposited one would receive 2.38% of the platform fees and 9.46% in RDNT token rewards.
If a loan is taken out against the deposited USDT, then there’s a 15.16% interest charge on the money borrowed. However, one would also receive 26.95% in RDNT token rewards.
The total rewards paid for depositing and borrowing USDT would be:
(2.38% + 9.46) + (26.95% – 15.16%) = 23.63%
Where else can you earn these kinds of returns on idle assets?
Where Can You Learn to use DeFi?
If you’re ready to deploy crypto assets into DeFi but need more confidence to take the first step, consider signing up for the Let’s Crypto! Bootcamp. Our signature training will grow your investing confidence and help you build your investing plan.
Not ready to signup for the Bootcamp? No problem. You can learn more about it from this blog post.
